What is Arabidopsis thaliana?
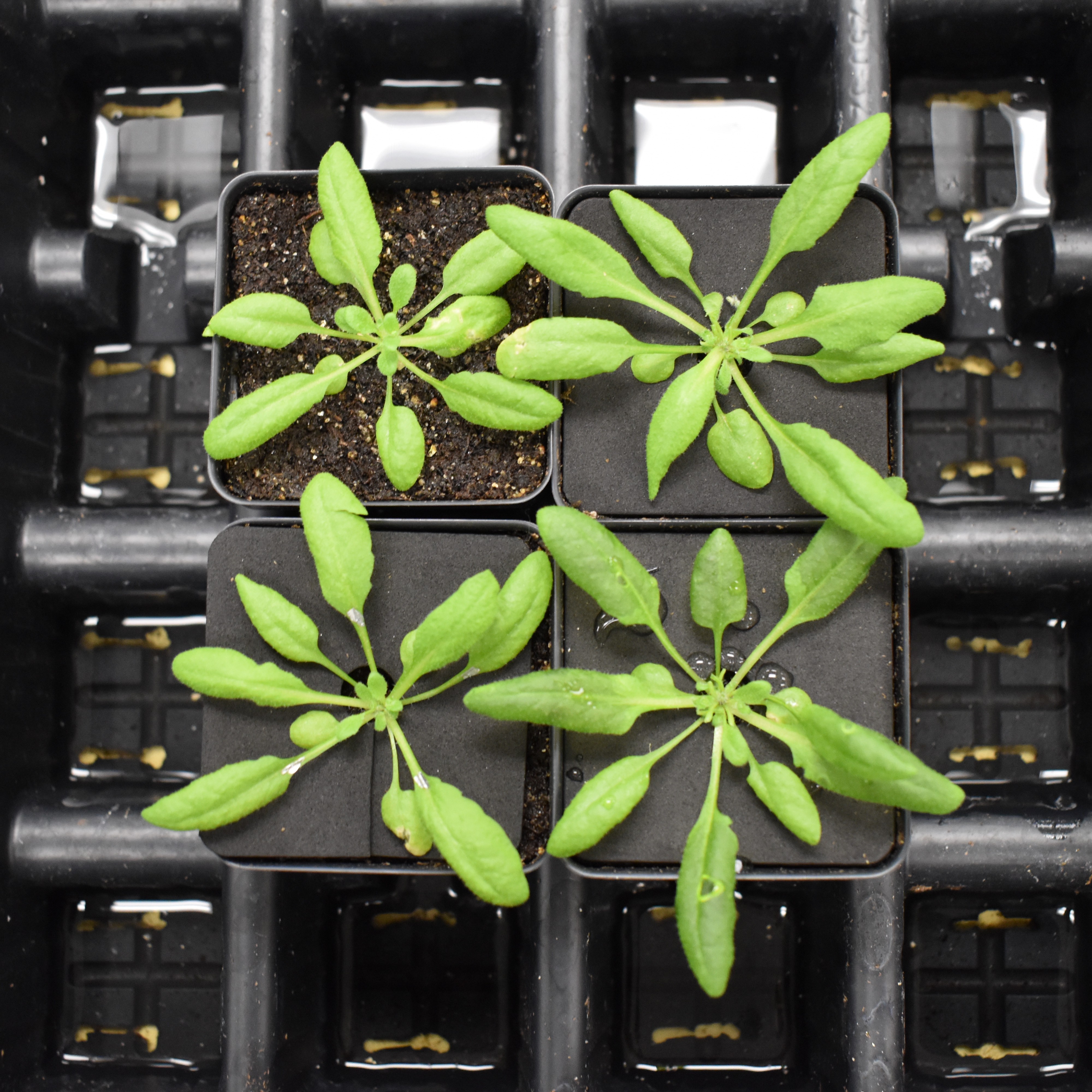

Arabidopsis thaliana – also known as Arabidopsis or thale cress – is a small flowering plant often used in plant research. It is a model organism for plant biology and genetics.
What is a model organism and why do we use them?
Model organisms are species which are easy to grow and manipulate that are extensively studied to gain novel insight into fundamental biological processes. They often lend themselves to genetic analysis and engineering.
For example, scientists study Drosophila, or the fruit fly, because they have many genes common with humans, sharing 60% of our genome. This allows researchers to study specific aspects of human biology without needing human subjects.
Other model organisms include, but are not limited to:
- Mice for understanding disease in humans
- Yeast for understanding cellular processes in humans
- Escherichia coli, or E. coli, for understanding microbiology and genetics
In plant biology, the first genetic model organism popularized was Arabidopsis thaliana.
What makes Arabidopsis a good model organism?
There are a number of factors that make Arabidopsis a good model organism.
With its small size and hardiness as a weed, it requires very little to keep it alive in the laboratory: small incubators, light, air, water, and minerals.
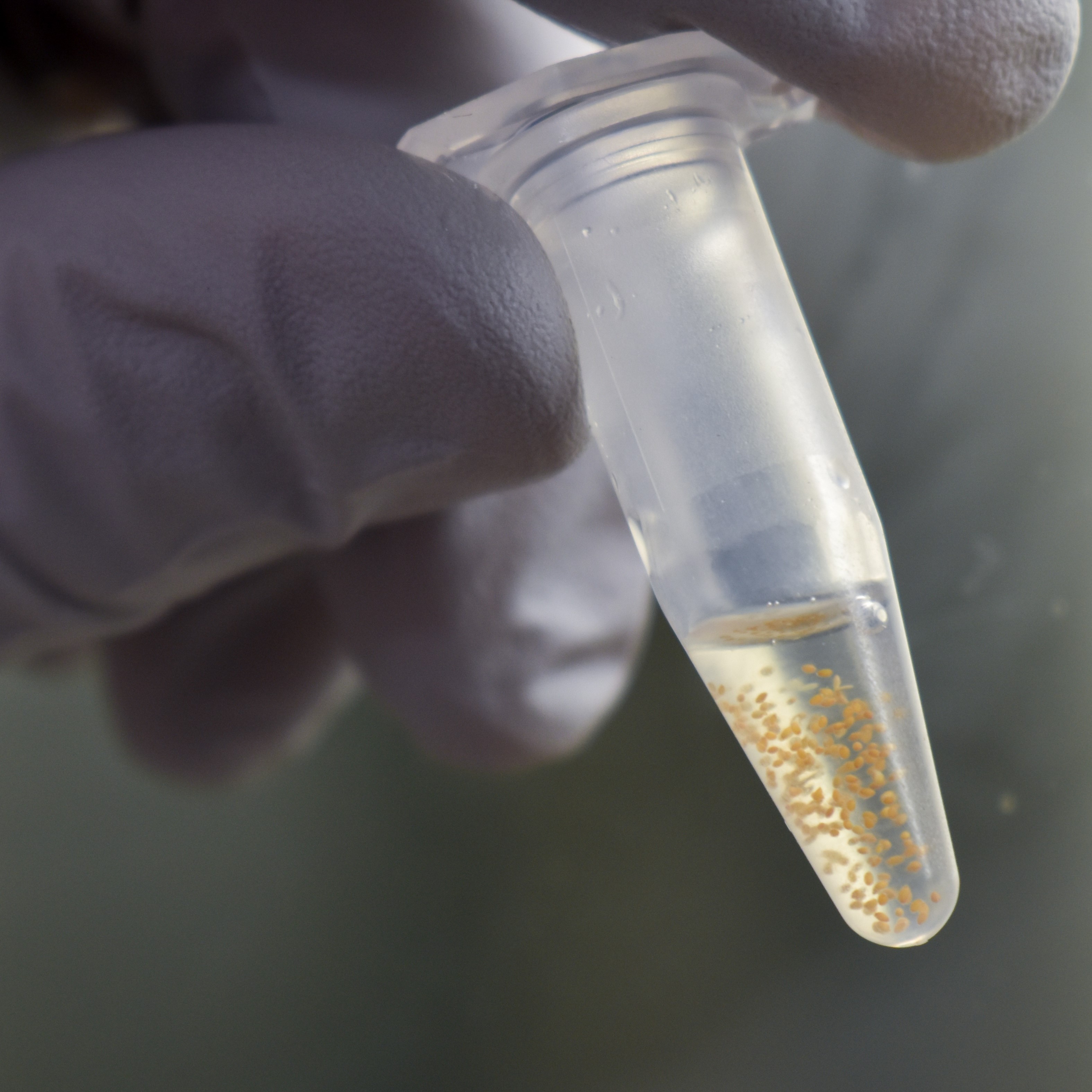
It has a fast life cycle. Arabidopsis can go from a seed to producing its own seeds in six weeks. It also can produce up to 10,000 seeds per plant, giving researchers an abundance to work with.
Arabidopsis has a relatively small genome, meaning an organism’s complete set of genetic blueprint which contains all the information it needs to develop and function. Arabidopsis has a genome size of around 135 Mb (megabase) pairs. This is tiny when compared with other well-studied plants. Corn, for example, has 2.4 Gb (gigabase) pairs, and wheat has 17 Gb pairs.
Why do scientists look at genes?
Arabidopsis was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, the project finishing in 2000. Genome sequencing is an important tool in molecular biology, allowing scientists to observe which genes cause certain traits.
For example, if we want plants that survive better in the heat, we may start by looking at a plant that is already adapted to do so. Which genes make this plant less susceptible to heat stress? Looking at its genetic structure, scientists may find a gene that allows the plant to be resilient to heat. That gene can be inserted into a different plant, i.e. a crop plant. Scientists can then look at how the genetically modified plant acts differently than its wild-type counterpart to gain scientific knowledge or to improve a crop to be more productive in a changing environment.
This is similar to how we got the crops we eat today, through a process known as selective breeding. For example, take the banana. Wild bananas are full of seeds and are not as tasty as the Cavendish banana you buy in the grocery store. Growers took bananas that had less seeds or that tasted better and bred them together. They then took the most desirable offspring of that union and kept breeding until they ended with a banana that is fit for mass human consumption.
Breeding for certain traits has the same end goal as genetically modifying plants in a lab, although genetically modifying plants takes much less time. By creating plants with specific genes, whether we are trying to make heartier plants to survive in changing environmental conditions or create crops that taste better, using genetic approaches is key.
Where is Arabidopsis found in nature?
Arabidopsis is found in temperate regions and is native to Europe, Asia and East Africa. It has been introduced to and naturalized in North America and Australia.
It likes sandy or gravelly soil and can be found growing on parking lots or along railways.
Is Arabidopsis edible?
Yes, but sources say it isn’t very good. It can be used in salad or sauteed, like mustard greens.
Arabidopsis is from the family Brassicaceae, which also contains cabbage, kale, broccoli, turnip and radish. Eating any of these will not give you the same experience as eating Arabidopsis, but it will likely taste better.
What scientific discoveries have been made using Arabidopsis?
Numerous scientific discoveries have been made, some right here at Michigan State University.