News
July 24, 2023
Research from the Brandizzi lab, led by postdoc Naveen Sharma, helps to better characterize the role of carbonic anhydrases in Arabidopsis thaliana, focusing on βCA1 and βCA5.
May 16, 2022
As our planet’s climate continues to be unpredictable, understanding how plants respond to adverse environmental conditions becomes essential. Improving crop productivity will be vital to feed the nine billion people estimated to be alive in 2050.
April 27, 2022
Spartan research in the lab of Cheryl Kerfeld could lead to efficient, low-cost chemical reactions for valuable products with help from teensy compartments made by bacteria.
April 12, 2022
Spartans in the Kramer lab discover how a plant biochemical could lead to novel approaches for growing crops that are more resilient to fluctuating temperatures.
December 22, 2021
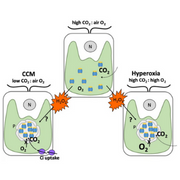
A structure that helps algae photosynthesize when carbon dioxide levels are low may also play a role during hyperoxia conditions.
May 20, 2021
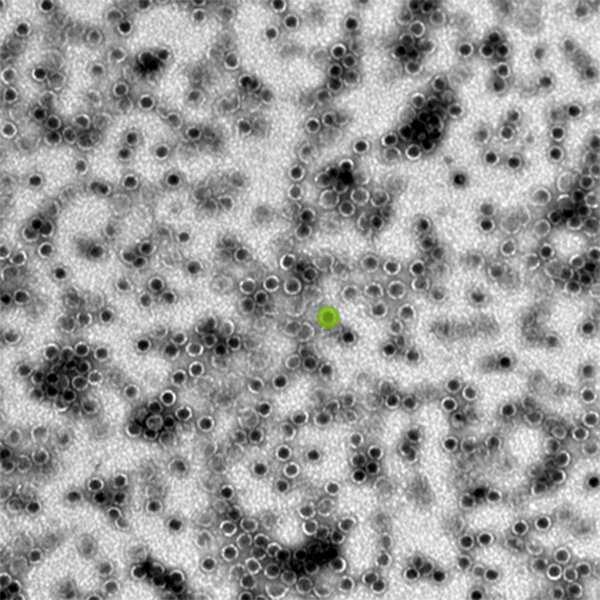
A new AI system, called DeepLearnMOR, can identify organelles and classify hundreds of microscopy images in a matter of seconds and with an accuracy rate of over 97%. The study illustrates the potential of AI to significantly increase the scope, speed, and accuracy of screening tools in plant biology.
May 13, 2021
The study reports that the activity levels of the carbon metabolism protein, G6PDH, are related to decreased production of pollen in bean flowers. As global temperatures rise, some bean crops, including Michigan-grown varieties, might be more sensitive to higher heat levels.
March 16, 2021
Berkley Walker is leading a new, nearly $1 million National Science Foundation grant effort to better understand photorespiration, a natural process that saps plants’ productivity.
February 23, 2021
A new study from Michigan State University is shedding light on how plants could potentially become more efficient at photosynthesis. The long-term implications of this research range from improved agricultural productivity to predicting the effects of climate change.
December 4, 2020
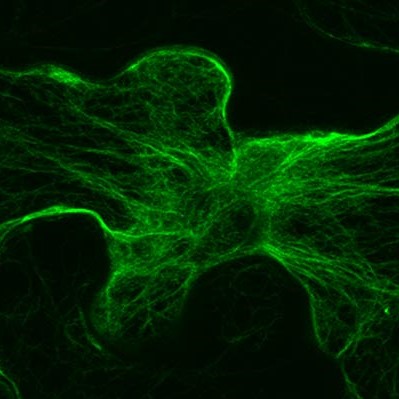
A new study from Michigan State University identifies a missing link which controls plant immunity and plants’ ability to maintain their cytoskeleton – the frame that both gives plant cells their shape and that serves as a highway for materials to move inside these cells.
October 8, 2020
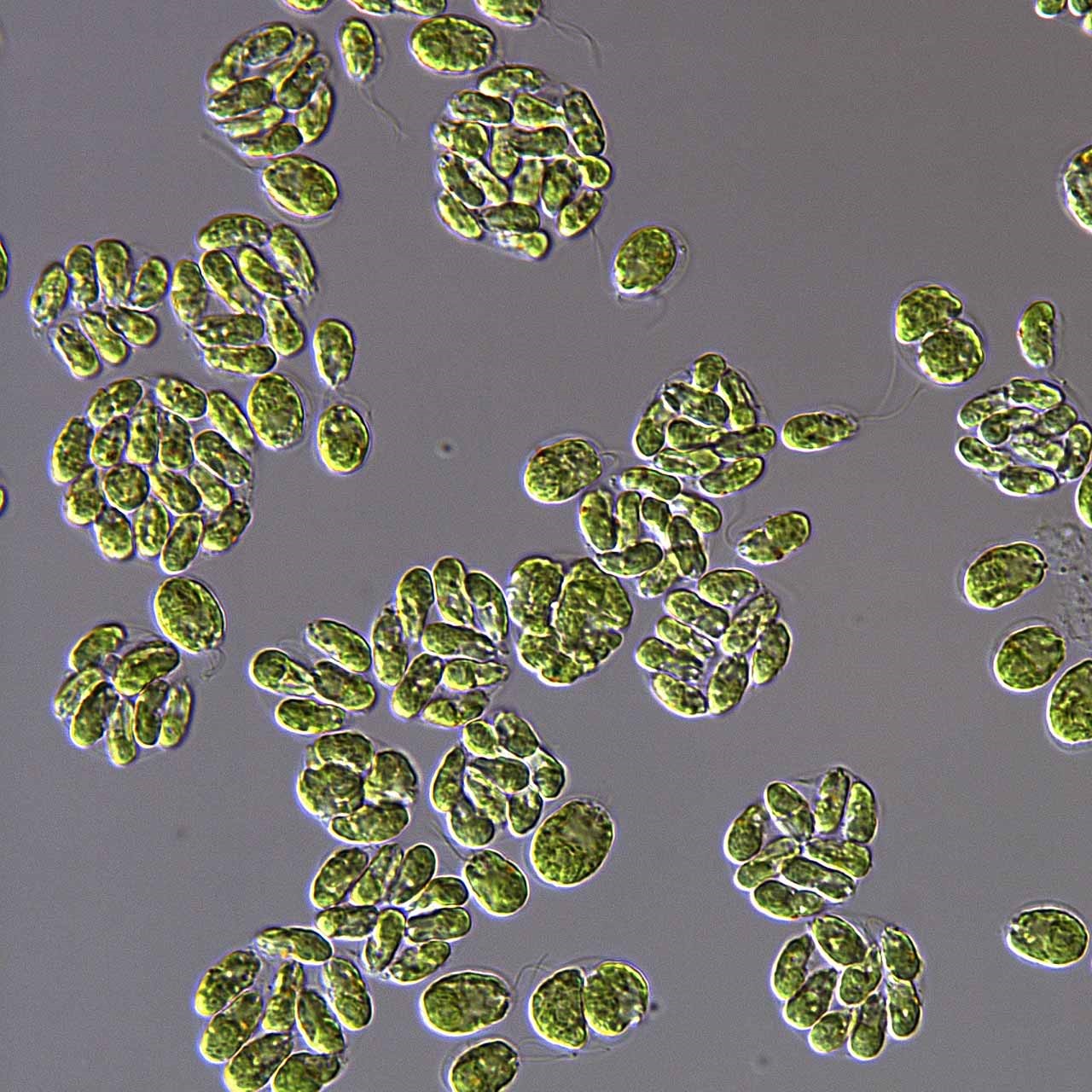
A new study delves into how algae manage cell division processes when they suffer from starvation. The finding has implications for biofuel technologies, given that algae have the potential to become a sustainable source of high value oils.
September 3, 2020
Cheryl Kerfeld was recently interviewed by the journal BioTechniques. In the video, she discusses bacterial microcompartments and her work on the Proteo Cell Project, an effort to create the first cell without any lipids present.
August 31, 2020
The lab of Thomas D. Sharkey have characterized a sucrose transporter protein found in common beans. The recently discovered protein, called PvSUT1.1, could help us understand how beans tolerate hot temperatures.
July 16, 2020
This long-from article details how our scientists are working to unlock the secrets of photosynthesis, an effort which might spur an agricultural revolution and lead to innovative energy and industrial technologies. The article appears in Futures, a magazine produced twice per year by Michigan State University AgBioResearch.
July 6, 2020
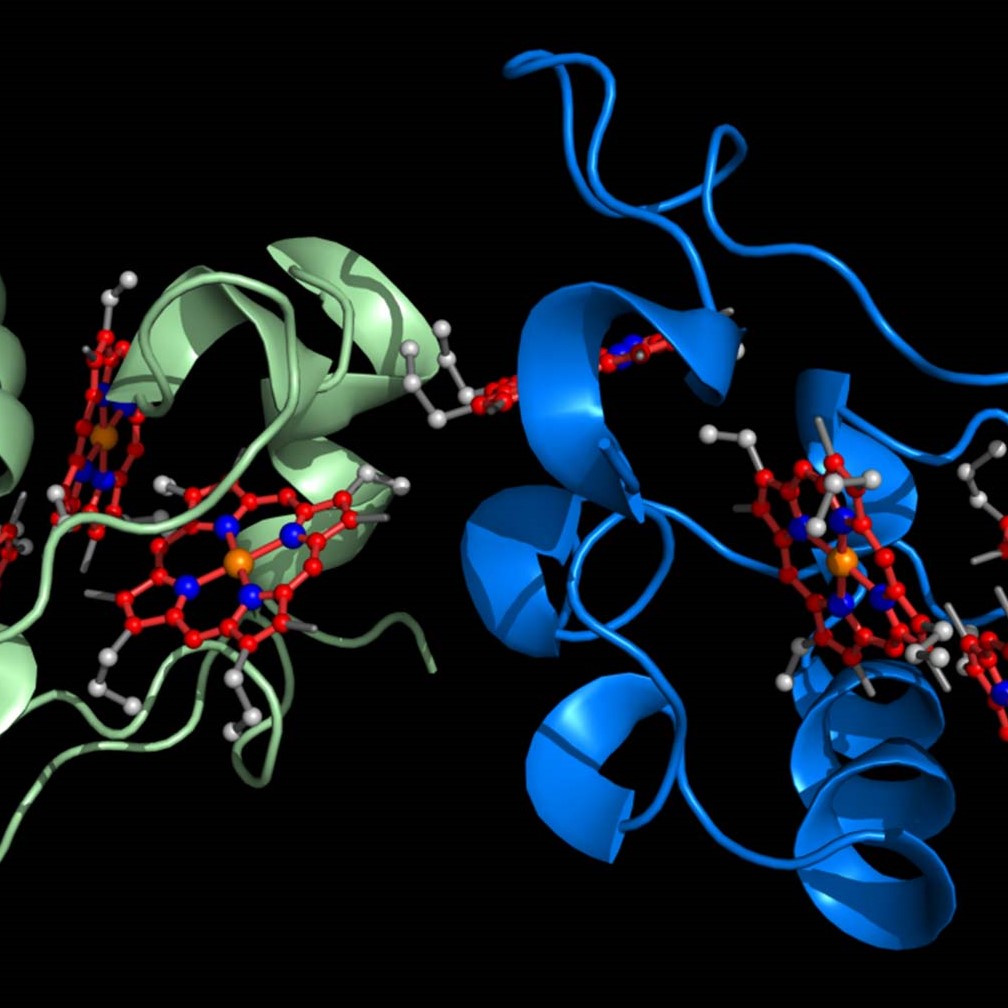
The work explores how electrons can move across long distances within biomaterials, such as proteins. Understanding the factors that control electron transfer in a biological context is critical to advances in diverse fields, including bioenergy, biosynthesis and disease.
June 24, 2020
A new paper reveals how nature has come up with solutions for photosynthetic organisms to safely harvest sunlight. The paper is included as a chapter in a new book, Photosynthesis in Algae: Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms, published by Springer.
May 29, 2020
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has awarded the Michigan State University-DOE Plant Research Laboratory a three-year (2020-2023), $11.25 million DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences competitive renewal grant to continue its innovative photosynthesis research.
May 26, 2020
Scientists have established a new method to quantify how much cyanobacteria assimilate carbon in the process of photosynthesis. The method assesses carbon assimilation over a stretch of time. It also better factors in a wider range of environmental variables, such as changing carbon dioxide levels or varying light intensities.
April 9, 2020
In a new study, published in the journal Nature, the lab of Sheng Yang He shows how plant genes select which microbes get to live inside their leaves in order stay healthy. This is the first study to show a causal relationship between plant health and assembly of the microbial community in the phyllosphere.
April 7, 2020
In plants, elevated defense tends to inhibit plant growth. New research suggests plants have a metabolism-sensing mechanism that may mediate between growth and defense functions.
March 5, 2020
New research is refining our understanding of how light wavelengths impact how plants develop their chloroplasts.
February 18, 2020
The protein, peroxiredoxin Q, is known to maintain a healthy balance of chemicals and energy levels in chloroplasts. The new research shows the protein also impacts the system that produces chloroplast membranes.
February 11, 2020
The CAMTA system - which is known to protect plants from cold weather - plays a newly discovered role: when bacteria invade a leaf, CAMTA warns neighboring, unaffected leaves to prepare for invasion.
February 3, 2020
When algae get stressed, they hibernate and store energy in forms that we can use to make biofuels. Understanding how stress impacts algal hibernation could help scientists lower the cost of biofuels production.
January 20, 2020
Recent models are telling us that, as our climate warms up, pests will cause more damage to crops. But these models do not factor how infested plants react to rising temperatures. If we do, plants may suffer a worse fate.
January 8, 2020
Berkley Walker's DNA synthesis proposal has been selected by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, to study how high temperatures impact plant enzymes that support photosynthesis.